Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is redefining the way organizations operate, enabling businesses to make faster, data-driven, and more accurate decisions. With the help of AI-powered tools, companies can automate complex workflows, identify trends in real-time, and make informed strategic choices that were once limited to expert analysts. These tools have democratized business intelligence by providing intuitive platforms that allow both technical and non-technical users to interact with data seamlessly. This paper explores various categories of AI tools—including coding assistants, visualization systems, spreadsheet optimizers, business intelligence platforms, and design tools—and explains how they contribute to improving business decision-making. Each section details what these tools do, their advantages and limitations, and best practices for using them efficiently.
1. AI Tools for Coding and Automation
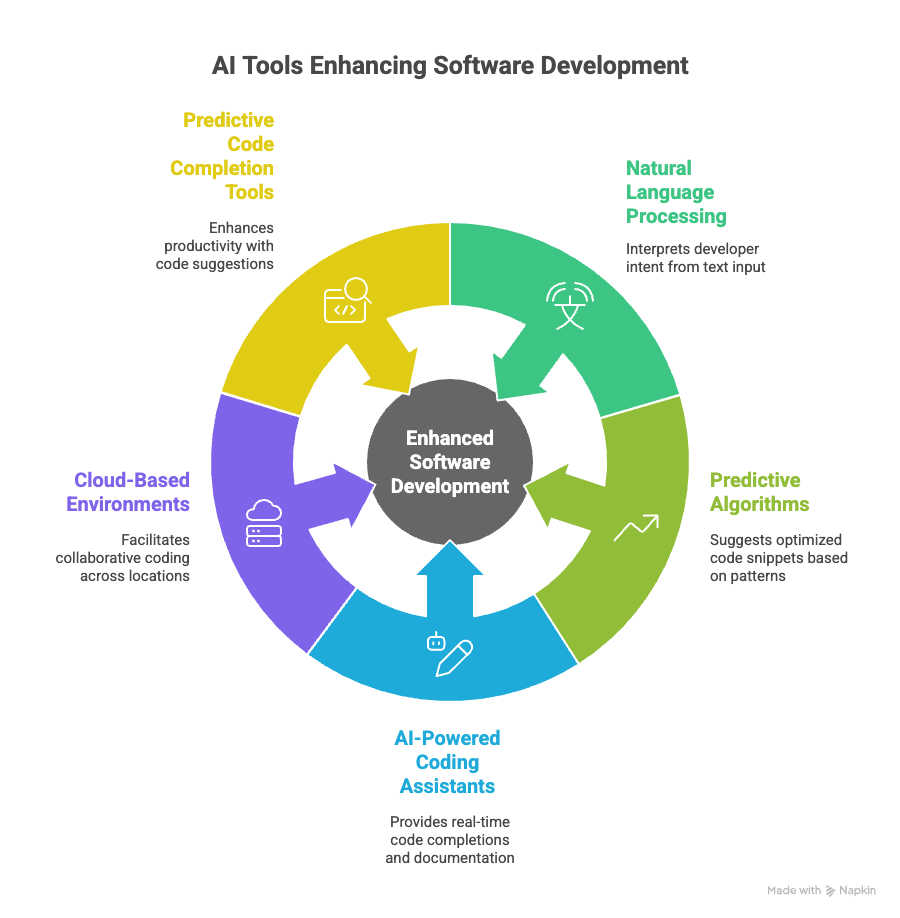
AI-assisted coding tools streamline software development, reduce the need for repetitive manual coding, and allow businesses to deploy technical solutions faster. By integrating natural language processing and predictive algorithms, these tools can interpret developer intent, suggest optimized code snippets, and automatically debug common programming errors. This not only accelerates the software development lifecycle but also improves code quality and team collaboration. Such tools are increasingly used by startups, IT firms, and automation engineers to build applications that align with organizational objectives.
Examples:
• GitHub Copilot – An AI-powered coding assistant developed by GitHub and OpenAI that suggests real-time code completions and documentation based on contextual understanding of the project.
• Replit Ghostwriter – A cloud-based environment that uses machine learning to assist with coding and debugging collaboratively, ideal for teams working remotely or across different time zones.
• Tabnine – A predictive code completion tool that supports multiple programming languages, enhancing development productivity in enterprise projects.
Pros: Boosts productivity, minimizes coding errors, and accelerates project timelines by automating repetitive tasks. Cons: May generate inaccurate or incomplete code in complex scenarios; requires human review to ensure compliance and accuracy. Efficient Use: Combine AI code suggestions with manual code validation and version control practices to maintain long-term code reliability and scalability.
2. AI Tools for Data Visualization and Graphing
AI-powered visualization platforms transform raw data into interactive dashboards and dynamic visual stories, enabling business leaders to interpret patterns and make data-backed decisions. These tools use advanced analytics and predictive modeling to uncover hidden relationships within datasets that might otherwise go unnoticed. From financial trend analysis to customer segmentation, AI visualizers help organizations monitor performance metrics and forecast future scenarios effectively.
Examples:
• Tableau with Einstein Analytics – Integrates AI-driven analytics to identify outliers, predict trends, and visualize business data for real-time decision-making.
• Microsoft Power BI – Offers automated insights and natural language querying, allowing users to generate detailed reports without technical expertise.
• ChartGPT – Uses AI to generate professional-grade charts and visual reports from text prompts, reducing the time needed for manual chart creation.
Pros: Enhances data comprehension, supports predictive insights, and allows decision-makers to visualize KPIs intuitively. Cons: Requires accurate, clean data and can be expensive for smaller firms to maintain licenses. Efficient Use: Align visualization dashboards with organizational KPIs to ensure that AI-generated insights directly inform strategic planning and operational efficiency.
3. AI Tools for Spreadsheet Management
Spreadsheets remain a vital part of business decision-making, but managing them manually is often inefficient and prone to human error. AI-powered spreadsheet tools eliminate redundancy by automating formula creation, cleaning datasets, and generating insights from raw entries. These tools can also interpret natural language commands, making spreadsheet management more accessible for non-technical users.
Examples:
• SheetAI for Google Sheets – Allows users to perform calculations, visualize data, and interpret trends using simple text-based commands.
• Excel Copilot – Microsoft’s AI integration in Excel that helps users automate data entry, create complex formulas, and visualize business metrics efficiently.
• Rows.com – A collaborative spreadsheet tool that combines API integration and visualization capabilities for streamlined business workflows.
Pros: Increases data accuracy, reduces workload, and supports faster decision-making by automating repetitive tasks. Cons: Heavily dependent on input quality and can face limitations when dealing with large, unstructured datasets. Efficient Use: Combine AI spreadsheets with cloud-based databases for real-time updates and ensure proper data governance to maintain accuracy.
4. AI Tools for Business Analysis and Decision Support
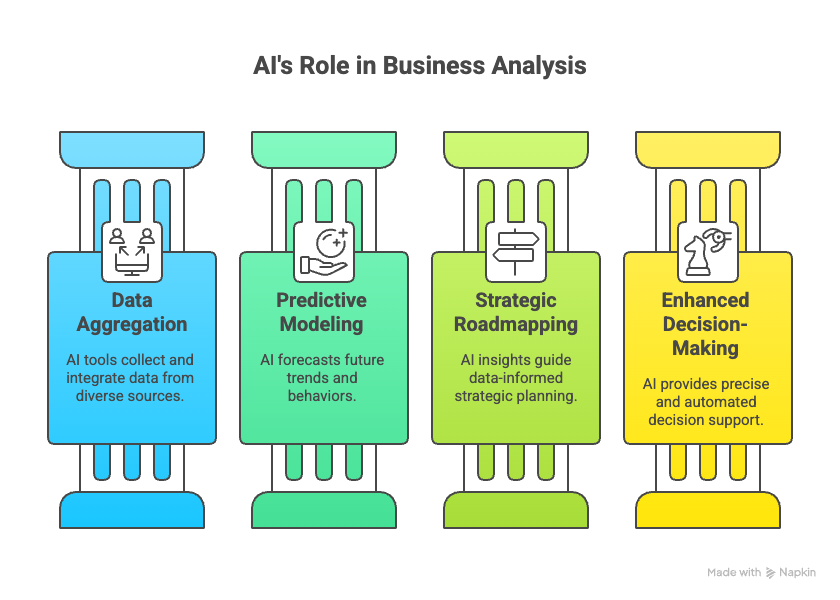
AI-driven business analysis tools are transforming how organizations interpret and act on large data volumes. These platforms aggregate information from multiple sources, including financial systems, marketing platforms, and customer feedback, to provide comprehensive insights. Through predictive modeling, they can forecast future trends, customer behaviors, and operational bottlenecks. Business leaders can then use these insights to design strategic roadmaps that are data-informed rather than intuition-based.
Examples:
• IBM Watson Studio – Offers data visualization, predictive analytics, and natural language processing for informed decision-making across industries.
• Google Cloud Vertex AI – A managed machine learning platform that simplifies building and deploying AI models for business forecasting and optimization.
• MonkeyLearn – Specializes in natural language processing to analyze text data such as customer reviews, enabling sentiment and topic analysis.
Pros: Empowers leaders with predictive foresight, enhances analytical precision, and automates decision modeling. Cons: Implementation complexity and data privacy concerns may limit accessibility for smaller organizations. Efficient Use: Integrate AI insights with human expertise to validate predictions and improve decision accountability.
5. AI Tools for Presentation and Visual Communication
AI-powered design platforms have transformed business communication by enabling professionals to create impactful presentations and visuals effortlessly. These tools use generative design techniques to suggest optimal layouts, color schemes, and narratives, helping teams present complex information in a visually appealing way. They are especially valuable for professionals who need to communicate insights from data analytics to stakeholders without technical jargon.
Examples:
• Beautiful.ai – Uses machine learning to automate design layouts and ensure professional consistency across slides.
• Tome – Converts business concepts into visually rich narratives, incorporating text, visuals, and embedded analytics seamlessly.
• Canva Magic Studio – Offers AI-assisted content generation for creating visuals, infographics, and business reports with minimal effort.
Pros: Enhances communication effectiveness, saves design time, and ensures brand consistency. Cons: May restrict creative control and customization for advanced users. Efficient Use: Combine AI-generated templates with human storytelling and brand identity to deliver engaging and authentic presentations.
Conclusion
AI tools are reshaping the business decision-making process by combining automation, predictive intelligence, and visual clarity. From streamlining code development to visualizing data insights and crafting compelling presentations, these technologies improve both operational and strategic efficiency. Businesses that integrate AI responsibly—balancing automation with human judgment—are more likely to achieve long-term sustainability and innovation. As AI evolves, its applications in business intelligence will continue to expand, making data-driven decisions the foundation of competitive success.
References
- 1. Forbes Technology Council. (2023). The Role of AI Tools in Business Automation. https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestechcouncil/2023/04/12/the-role-of-ai-tools-in-business-automation/
- 2. Microsoft. (2024). Power BI and Copilot Integration. https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/power-bi/transform-model/ai-insights
- 3. IBM. (2023). Watson Studio Overview. https://www.ibm.com/products/watson-studio
- 4. Google Cloud. (2024). Vertex AI Documentation. https://cloud.google.com/vertex-ai
- 5. Canva. (2024). AI Design Tools for Business. https://www.canva.com/magic-studio/
Author:
Nafiz Imtiaz
